Ways to save electricity
In the summer the Japanese government asked people to save electricity.
Why?
What have you or your company been doing to save electricity?
Describe these ways to save electricity:
Turn off lights you aren’t using. Many companies are turning off office lights at lunchtime
Turn off your air-con in empty rooms and set the temperature a little higher than usual
Unplug appliances you aren’t using (lamps, TV, kettle)
Use blinds or curtains to block hot sunlight
Shops are turning off unnecessary lights (e.g. for signs)
install solar panels - the government will provide subsidies
Buy new eco-friendly fridges and air cons. The government will provide subsidies
Clean your air con filter (once) every 2 weeks
After the Fukushima Earthquake in 2011, Japan turned off ALL of it’s Nuclear Power plants. Japan had 54 nuclear power plants that supplied 30% of Japan’s energy.
How do they produce energy now?
Japan decided to focus on burning LNG to meet it’s green targets. Now we realize this was a risky strategy.
The skyrocketing LNG prices are giving Japan confidence to restart Nuclear Power plants.
Do you think this idea will be accepted by people?
How many nuclear power plants are operating now?
Japan's energy sources 2020
Currently Japan has 6 nuclear power plants in operation
Japan plans to increase nuclear power generation to 22% by 2030.
Do you think the public or media will complain about this?
In the world, do you think countries use more renewable energy or nuclear energy?
Now renewable energy is 13% of the world’s power supply.
What kinds of renewable energy do you know? What are the pros and cons of each?
(all pictures are in Japan)
Japan is building both offshore and onshore wind farms. Which are better?
What is BIOMASS energy?
A start-up called "eRex" is converting coal plants in Japan to biomass plants. The company grows Sorghum in Vietnam and Philippines for it's fuel
Sorghum is cheap to grow and can be harvested 2-3 times a year
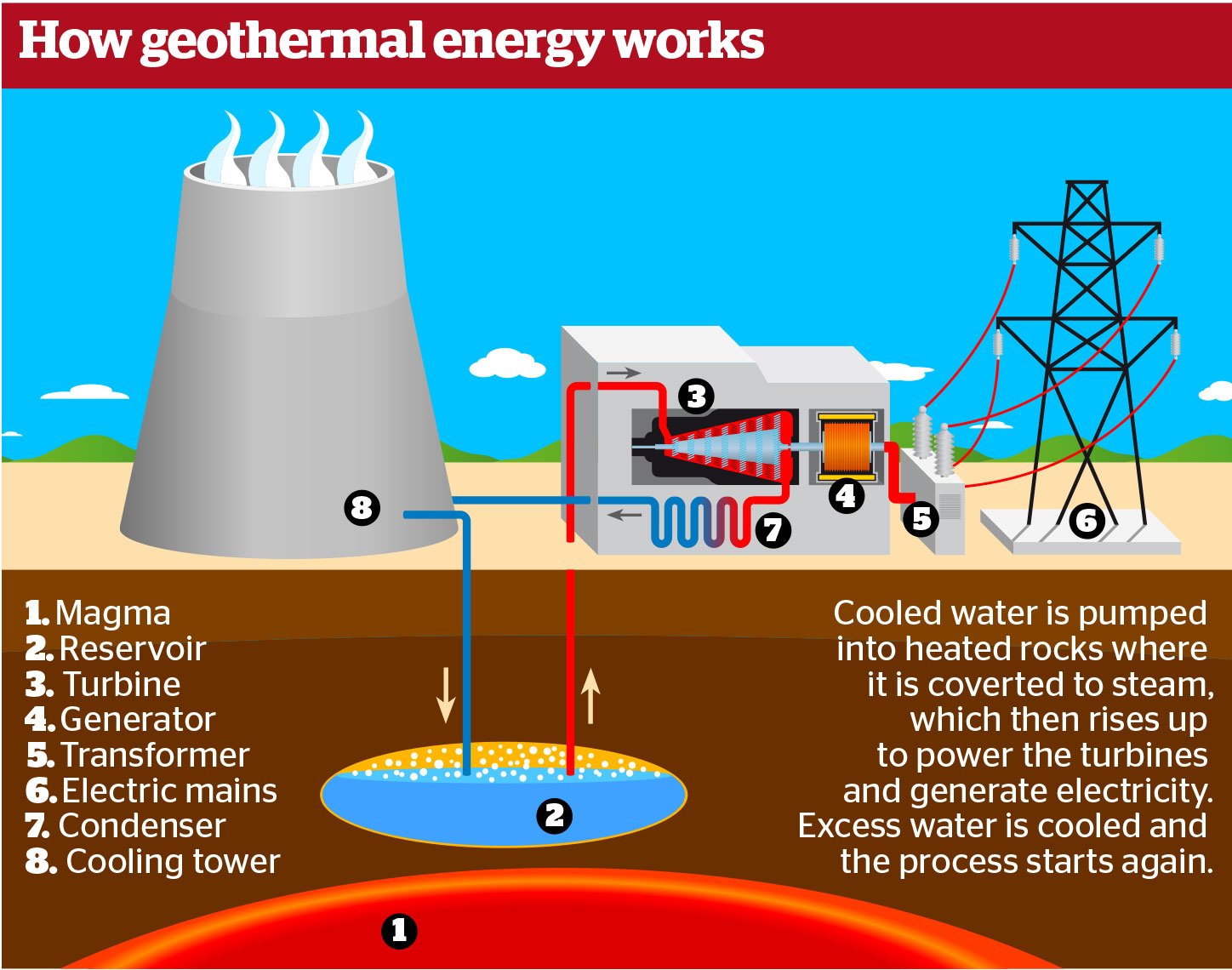
What is GEOTHERMAL energy?
The first geothermal plant in Japan was built in Beppu in 1924 - it was used to heat homes and cook food
In 1954 the first commercial geothermal plant opened.
There are only 20 geothermal plants in Japan
Type
Solar
Hydroelectric
Wind
Geothermal
Biomass
Pros
unlimited supply , clean
relatively reliable, night use
low cost, minimal maintenance, won’t run out.
no noise, very clean
cleaner than burning fossil fuels, not based on weather, coal plants can be converted to biomass
Cons
night time, winter, cost, (glare for neighbours)
environmental damage, water source must be reliable,
no wind, noise, birds
lots of water needed, earthquake risk, can’t power large cities
usually crops like corn, sugarcane are burned - competes with food suppliers
In 2030 Japan starts to use this to generate TIDAL energy. How do you think it works?
It’s called “Kairyu”
It will be placed in the Kuroshio Current which is one of the strongest in the world
It will be able to position itself for optimal power generation
Kairyu will be floated to the surface for maintenance